Texas Instruments Incorporated (NASDAQ:TXN) of Dallas, TX, is an American technology company which designs and fabricates semiconductors which are sold to designers and manufacturers of electronic devices from all over the world. Recently, Texas Instruments pulled the curtain away from its integrated battery monitor and protector device, an industry first for smart battery management solutions in electric vehicles and grid energy storage systems. At the upcoming Consumer Electronics Show in January, Texas Instruments will showcase a lineup of new semiconductor technologies with applications in advanced driver assistance systems and wearables. The company also recently announced a $2.8 investment with Dallas County Community College for the creation of an associate degree program in electrical engineering technology.
In late October, Texas Instruments released its earnings report for the third quarter of 2015, announcing a decline in quarterly revenue of about 2 percent from 2014’s third quarter, to $3.429 billion down from $3.501 billion. The corporation did announce some good 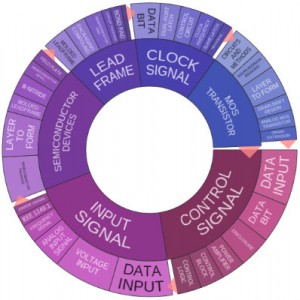 news in its core business of analog and embedded processing, which has seen increased sales every quarter for nine consecutive quarters. With reduced quarterly revenues, it’s not surprising to see that Texas Instruments has drawn back slightly on its research and development expenditures, although the company did spend nearly $2 billion on R&D in the third quarter.
news in its core business of analog and embedded processing, which has seen increased sales every quarter for nine consecutive quarters. With reduced quarterly revenues, it’s not surprising to see that Texas Instruments has drawn back slightly on its research and development expenditures, although the company did spend nearly $2 billion on R&D in the third quarter.
Texas Instruments’ R&D activities are strong. The company placed 52nd overall in 2014 among all companies obtaining patents from the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office with 830 U.S. patents, an increase over its 2013 patent totals of 12.3 percent. According to the patent portfolio analysis tools available through Innography, Texas Instruments has earned 825 U.S. patents through most of 2015, putting it on pace to perhaps slightly eclipse its 2014 totals. As the text cluster posted here shows our readers, much of TI’s recent R&D has focused on control signals, input signals and semiconductor devices.
Texas Instruments’ Issued Patents: Improved Device Location and Coexistence of Wireless Networks
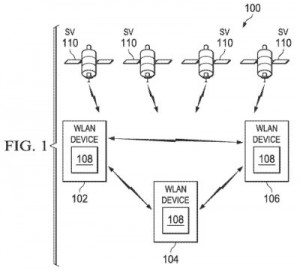 A few of the patents issued to Texas Instruments in recent weeks which caught our eyes are related to mobile device components, including the technology protected by U.S. Patent No. 9182493, titled Fine Time Assistance for Global Navigation Satellite Systems. It protects a method for synchronizing a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) receiver by receiving fine time assistance information transmitted by an assisting device connected to the same wireless local area network (WLAN), adjusting a time value of a GNSS clock based on the fine time assistance information, obtaining GNSS codes of a GNSS positioning signal based on the adjusted time value extracting a departure time from a received fine time assistance information measuring an arrival time at a wireless device, estimating a value for propagation delay time within the wireless device, computing clock bias between the device and the assisting device based on the departure time, arrival time and value for propagation delay, and then adjusting the time value based on the clock bias. This innovation is intended to reduce the amount of time that a satellite positioning system takes to locate a wireless device by utilizing assisting devices over a WiFi network. Improvements to power supply components of computing devices are featured within U.S. Patent No. 9209700, entitled Magnetic Sensing Technique for Power Supply Systems. It discloses a power supply system having a transformer with multiple windings that are magnetically coupled, a switch stage that generates a current induced by a secondary winding through a primary winding in response to the activation of a switch based on a control signal generated based on a feedback voltage associated with an auxiliary winding, and then a feedback stage coupled to the auxiliary winding with a discriminator that determines a zero-current condition associated with the current induced in the secondary winding; the discriminator further comprises a window comparator that establishes a window of acceptable magnitudes for the change in slope of the feedback voltage. This power supply system configuration for power circuits, such as discontinuous flyback power regulators, enables the measuring of output voltage while maintaining isolation between secondary-side and primary-side components.
A few of the patents issued to Texas Instruments in recent weeks which caught our eyes are related to mobile device components, including the technology protected by U.S. Patent No. 9182493, titled Fine Time Assistance for Global Navigation Satellite Systems. It protects a method for synchronizing a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) receiver by receiving fine time assistance information transmitted by an assisting device connected to the same wireless local area network (WLAN), adjusting a time value of a GNSS clock based on the fine time assistance information, obtaining GNSS codes of a GNSS positioning signal based on the adjusted time value extracting a departure time from a received fine time assistance information measuring an arrival time at a wireless device, estimating a value for propagation delay time within the wireless device, computing clock bias between the device and the assisting device based on the departure time, arrival time and value for propagation delay, and then adjusting the time value based on the clock bias. This innovation is intended to reduce the amount of time that a satellite positioning system takes to locate a wireless device by utilizing assisting devices over a WiFi network. Improvements to power supply components of computing devices are featured within U.S. Patent No. 9209700, entitled Magnetic Sensing Technique for Power Supply Systems. It discloses a power supply system having a transformer with multiple windings that are magnetically coupled, a switch stage that generates a current induced by a secondary winding through a primary winding in response to the activation of a switch based on a control signal generated based on a feedback voltage associated with an auxiliary winding, and then a feedback stage coupled to the auxiliary winding with a discriminator that determines a zero-current condition associated with the current induced in the secondary winding; the discriminator further comprises a window comparator that establishes a window of acceptable magnitudes for the change in slope of the feedback voltage. This power supply system configuration for power circuits, such as discontinuous flyback power regulators, enables the measuring of output voltage while maintaining isolation between secondary-side and primary-side components.
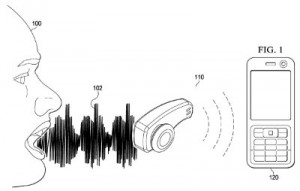 A cloud computing innovation which is meant to reduce the cost of providing speech and sound recognition in electronic devices is at the center of U.S. Patent No. 9177546, which is titled Cloud Based Adaptive Learning for Distributed Sensors. It claims a method for operating a sound recognition sensor by receiving an analog signal containing a signature sound, extracting sound parameter information from the analog signal, comparing the parameter information to a locally stored sound parameter reference to detect when the signature sound is received, generating a trigger signal based on the detection of a signature sound, sending a portion of the extracted sound parameter to a remote training location for adaptive training when a signature sound detection error occurs and receiving an updated sound parameter reference from the remote training location in response to the adaptive training. This cloud-based system is designed to reduce the significant power requirements of acoustic sensors implemented in order to perform voice or sound recognition. The provisioning of low-cost components for electronic devices is also discussed within U.S. Patent No. 9163941, entitled System and Method for Implementing Low-Cost Electronic Gyroscopes and Accelerometer. It protects an apparatus having two propagation paths formed on a substrate which are essentially the same shape, an oscillator coupled to both propagation paths applying different signals to either propagation path, a phase locked loop (PLL) coupled to both propagation paths and the oscillator and then detection circuitry coupled to the PLL to measure the phase difference between the two signals to determine physical movement. This type of component can serve as an accelerometer or gyroscope without requiring expensive optical parts such as lasers or photodetectors implemented on an integrated circuit.
A cloud computing innovation which is meant to reduce the cost of providing speech and sound recognition in electronic devices is at the center of U.S. Patent No. 9177546, which is titled Cloud Based Adaptive Learning for Distributed Sensors. It claims a method for operating a sound recognition sensor by receiving an analog signal containing a signature sound, extracting sound parameter information from the analog signal, comparing the parameter information to a locally stored sound parameter reference to detect when the signature sound is received, generating a trigger signal based on the detection of a signature sound, sending a portion of the extracted sound parameter to a remote training location for adaptive training when a signature sound detection error occurs and receiving an updated sound parameter reference from the remote training location in response to the adaptive training. This cloud-based system is designed to reduce the significant power requirements of acoustic sensors implemented in order to perform voice or sound recognition. The provisioning of low-cost components for electronic devices is also discussed within U.S. Patent No. 9163941, entitled System and Method for Implementing Low-Cost Electronic Gyroscopes and Accelerometer. It protects an apparatus having two propagation paths formed on a substrate which are essentially the same shape, an oscillator coupled to both propagation paths applying different signals to either propagation path, a phase locked loop (PLL) coupled to both propagation paths and the oscillator and then detection circuitry coupled to the PLL to measure the phase difference between the two signals to determine physical movement. This type of component can serve as an accelerometer or gyroscope without requiring expensive optical parts such as lasers or photodetectors implemented on an integrated circuit.
A technology designed to maintain communication in sensor networks implemented in industrial or healthcare settings is described within U.S. Patent No. 9204486, which is titled Coexistence of Wireless Sensor Networks with Other Wireless Networks. This protects a wireless device with a first wireless transceiver that transmits to and receives from nodes in a wireless sensor network and control logic coupled to the transceiver causing the transceiver to transmit a wireless packet to a node coinciding with a break in transmissions for a second wireless network; the control logic also causes time synchronized channel hopping (TSCH) slot frames for wireless packet transmission in the wireless sensor network to be offset so they don’t coincide with transmissions made on the second wireless network. This technology addresses issues caused by the proliferation of wireless communications technologies, including WLAN or Bluetooth, which might use overlapping portions of wireless spectrum. We also took note of an innovation meant to serve a commercial need in mainstream data projectors which is outlined within U.S. Patent No. 9195123, 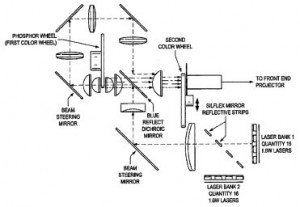 which is titled Projector Light Source and System, Including Configuration for Display of 3D Images. It protects an image projection system having a source emitting laser light having two wavelengths, a rotatable member having a first phosphor segment emitting light of a selected color upon receiving laser light of a first wavelength, a second phosphor segment emitting a second color upon receiving laser light of a second wavelength, two light transmissive segments for transmitting laser light; the system also includes light directing optics for directing laser light back to a location from which the rotatable member receives the laser light and a dichroic optical element for directing and transmitting laser light. The resulting projector system is capable of displaying 3D images utilizing a hybrid laser and a fluorescent emission light source.
which is titled Projector Light Source and System, Including Configuration for Display of 3D Images. It protects an image projection system having a source emitting laser light having two wavelengths, a rotatable member having a first phosphor segment emitting light of a selected color upon receiving laser light of a first wavelength, a second phosphor segment emitting a second color upon receiving laser light of a second wavelength, two light transmissive segments for transmitting laser light; the system also includes light directing optics for directing laser light back to a location from which the rotatable member receives the laser light and a dichroic optical element for directing and transmitting laser light. The resulting projector system is capable of displaying 3D images utilizing a hybrid laser and a fluorescent emission light source.
Patent Applications of Note: From Body Area Networks for Medical Devices to Background Music in Phone Calls
Short-range, low-power body area networks developed for medical purposes were featured by a pair of patent applications filed recently by Texas Instruments, including the innovation described within U.S. Patent Application No. 20150349839, entitled Ultra Wideband Modulation for Body Area Networks. It would protect a symbol modulation system having a symbol mapper configured to determine a time within a predetermined symbol transmission interval at which a transmission representative of the symbol will occur and then generate a single guard interval within the symbol transmission interval and positioned to terminate the symbol transmission interval. This body area network innovation establishes a physical layer which allows a receiver to identify and correct received data errors caused by channel issues. Physical layers in body area networks are also improved by the innovation discussed within U.S. Patent Application No. 20150350387, which is titled PHY Layer Options for Body Area Network (BAN) Devices. It claims a physical (PHY) layer method that involves performing body area network operations in a limited multipath environment using M-ary pre-shared keys (PSK), differential M-ary PSK or rotated differential M-ary PSK, and then transmitting BAN packets at a constant symbol rate. The use of physical layers to support BAN networking enables smarter medical devices, such as digital bandages that can measure and wirelessly transmit vital signs or pacemakers which can be fine-tuned after implantation.
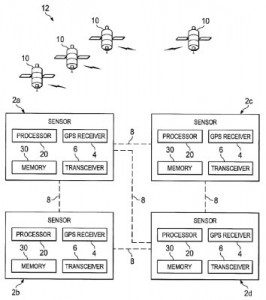 More effective satellite tracking systems are still on the radar for TI, as is evidenced by the filing of U.S. Patent Application No. 20150247928, entitled Cooperative Location Sensor Apparatus and System for Low Complexity Geolocation. It discloses a location sensor apparatus having a wireless receiver that receives communications signaling from a plurality of satellites, a wireless transceiver that communicates with another location sensor, an electronic memory and a processor operatively coupled with the receiver and transceiver to identify a given satellite based on received communications signaling, selectively decode orbital information related to the satellite, provide decoded orbital information to the location sensor via the wireless transceiver and selectively computing a sensor position based partially on the decoded orbital information. This invention is designed to improve the ability of location sensors to track satellites for communications, such as GPS navigation, when those sensors are being powered up from a cold-start after a long period of inactivity.
More effective satellite tracking systems are still on the radar for TI, as is evidenced by the filing of U.S. Patent Application No. 20150247928, entitled Cooperative Location Sensor Apparatus and System for Low Complexity Geolocation. It discloses a location sensor apparatus having a wireless receiver that receives communications signaling from a plurality of satellites, a wireless transceiver that communicates with another location sensor, an electronic memory and a processor operatively coupled with the receiver and transceiver to identify a given satellite based on received communications signaling, selectively decode orbital information related to the satellite, provide decoded orbital information to the location sensor via the wireless transceiver and selectively computing a sensor position based partially on the decoded orbital information. This invention is designed to improve the ability of location sensors to track satellites for communications, such as GPS navigation, when those sensors are being powered up from a cold-start after a long period of inactivity.
We were very intrigued to note the value-added service for telephone users which is at the center of U.S. Patent Application No. 20150317993, titled Method and System to Play Background Music Along with Voice on a CDMA Network. It would protect an apparatus for compressing an audio signal having a readable medium for retrieving or archiving date and a processor for performing a method that involves receiving a segment of an audio signal, selectively disabling suppression, filtering unsuppressed audio signal in a noise-suppression module, calculating an autocorrelation coefficient and a line spectral pairs (LSP) coefficient, predicting short-term and long-term coefficients according to the LSP coefficients, calculating bandwidth-expanded correlation coefficients, determining a type of packet in which to encode the segment based on the various calculated coefficients, selecting an encoding rate based on the noise suppression setting and forming the segment into a packet of the determined type and selected rate. This invention provides an efficient solution to providing background music during a telephone call, which is affected by the voice-centric signal attenuation techniques of enhanced variable rate codecs.
The reduction of delays in accessing software or hardware resources in a computing device is the goal of the innovation that would be protected by U.S. Patent Application No. 20150324208, entitled Fast Startup Behavior Control of a CPU. It claims a method for reducing startup time of a microcontroller that involves reading user code from storage, determining when an inter-process communication (IPC) has occurred, returning and reading a read value when an IPC hasn’t occurred, determining whether a system is ready when an IPC has occurred, determining whether a communication request has been made when the system is ready, returning and reading a debug entry address when a communication request has been made, determining whether a valid cold start address had been provided when the communication request has not been made and providing a BSL entry address when the valid cold start address has been provided.
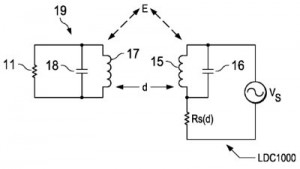 The ability to measure electrical resistance of components which are not accessible to typical resistance measuring equipment is enabled by the technology discussed within U.S. Patent Application No. 20150293158, entitled Contactless Resistance Measurement. It discloses a method for non-contact resistance measurement by providing a resistive element that is physically connected as part of a passive electrical circuit, using an electromagnetic field to produce an excitation in the passive electrical circuit and determining the resistance of the resistive element based on an effect of the excitation on the electromagnetic field. This innovation provides a simple and cost-effective manner for measuring resistance in automotive machinery or blood/reagent mixtures.
The ability to measure electrical resistance of components which are not accessible to typical resistance measuring equipment is enabled by the technology discussed within U.S. Patent Application No. 20150293158, entitled Contactless Resistance Measurement. It discloses a method for non-contact resistance measurement by providing a resistive element that is physically connected as part of a passive electrical circuit, using an electromagnetic field to produce an excitation in the passive electrical circuit and determining the resistance of the resistive element based on an effect of the excitation on the electromagnetic field. This innovation provides a simple and cost-effective manner for measuring resistance in automotive machinery or blood/reagent mixtures.
Finally, we were intrigued to explore an innovation for providing ultra high-definition (HD) video in computing hardware which is outlined within U.S. Patent Application No. 20150271494, which is titled Low Power Ultra-HD Video Hardware Engine. It discloses a video hardware engine having a video hardware accelerator unit, a shared memory coupled to the the accelerator unit, a scrambler that receives a largest coding unit from the video hardware engine and coupled to the shared memory, a video direct memory access (vDMA) engine coupled to the scrambler and an external memory coupled to the vDMA engine. This technology provides a low-power solution for a multi-format video hardware engine that can provide video at 4K resolution and at 60 frames per second.

![[IPWatchdog Logo]](https://ipwatchdog.com/wp-content/themes/IPWatchdog%20-%202023/assets/images/temp/logo-small@2x.png)


![[[Advertisement]]](https://ipwatchdog.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/2021-Patent-Practice-on-Demand-1.png)
![[Advertisement]](https://ipwatchdog.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/Patent-Litigation-Masters-2024-sidebar-early-bird-ends-Apr-21-last-chance-700x500-1.jpg)

![[Advertisement]](https://ipwatchdog.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/WEBINAR-336-x-280-px.png)
![[Advertisement]](https://ipwatchdog.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/2021-Patent-Practice-on-Demand-recorded-Feb-2021-336-x-280.jpg)
![[Advertisement]](https://ipwatchdog.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/Ad-4-The-Invent-Patent-System™.png)






Join the Discussion
One comment so far.
American Cowboy
December 29, 2015 09:48 amCool techie stuff.
Is TI still acting like a patent troll by getting other companies who have operations to pay royalties to TI for patents that TI does not itself commercialize?